Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia
February 14, 2026
Share This Article

If you build or buy suspensions for Russia, getting aligned with Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia is non‑negotiable. This guide translates the key standards, tests, and on‑terrain realities into a practical roadmap you can act on today. If you’re scoping a project now, share your vehicle type, terrain mix, and target homologation route—we can map tests, provide sample dyno plots, and draft a custom plan with timelines and budget.
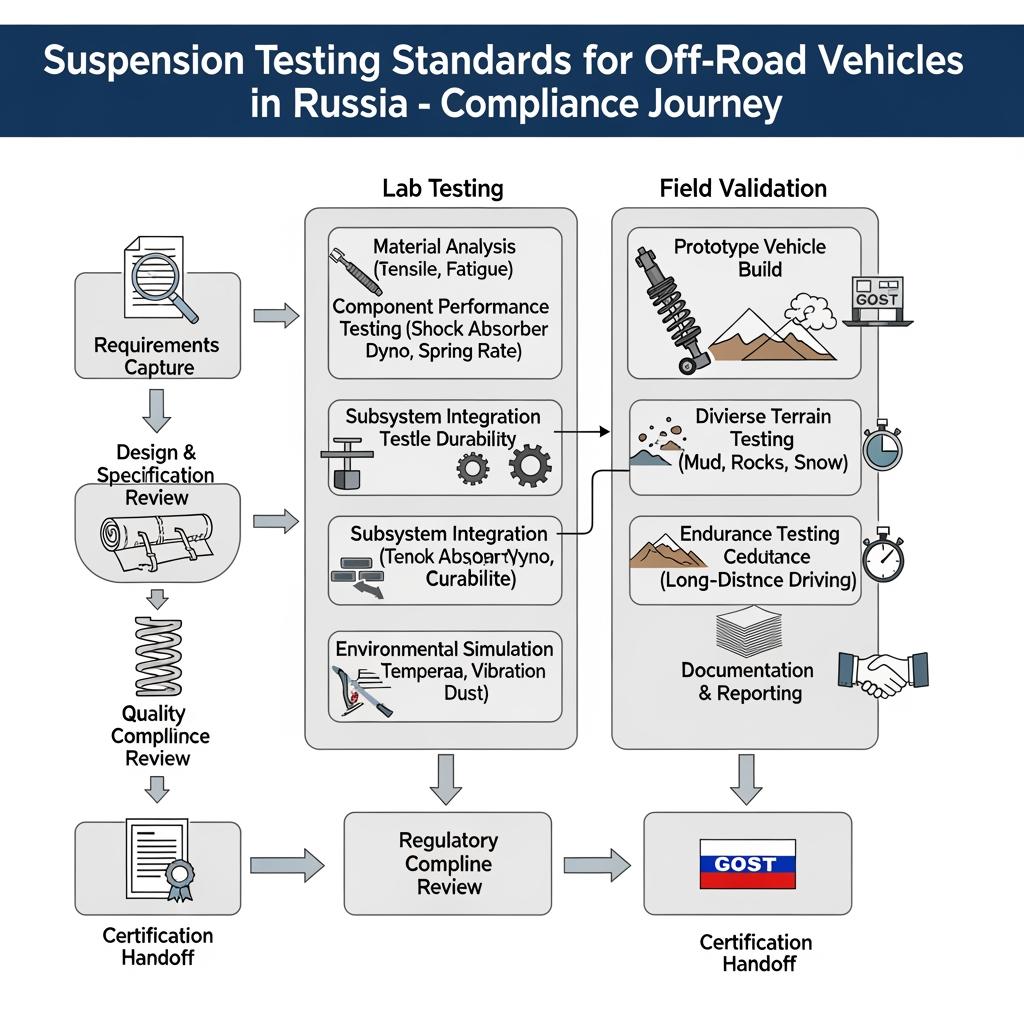
Overview of GOST Suspension Standards for Off-Road Vehicles
The backbone of suspension compliance in Russia is the Eurasian Economic Union technical regulation TR EAEU 018/2011 “On the Safety of Wheeled Vehicles,” supported by GOST/GOST R methods that adopt or mirror ISO/UNECE tests. For off‑road suspensions and shock absorbers, the emphasis is consistent: prove predictable damping, endurance in cold and abrasive conditions, corrosion resistance, and safe attachment under impact.
In practice, manufacturers assemble a test dossier that includes dynamometer curves across temperatures, endurance cycling, leak and seal integrity checks, corrosion exposure, and mounting strength evidence. Field validation under representative terrain (sand, mud, washboard, rocks, snow) often complements lab data. Documentation typically includes a Russian translation of the test summary, traceability of materials, labeling marks, and either a Declaration of Conformity or certification per the chosen route.
| Scope area | What gets verified | Typical method reference | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damping performance | Force–velocity curves, hysteresis, fade | Damper dyno across temperature range | Include −40°C runs for northern regions; align with Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia |
| Durability | Cycle endurance under heat and side‑load | High‑frequency bench cycling with thermal control | Watch for nitrogen pressure loss and cavitation onset points |
| Environmental | Corrosion, dust, mud, water, salt | Salt fog, dust ingress, slurry splash | Coating and seal selection drive pass/fail outcomes |
| Mechanical integrity | Mount pull‑out, weld fatigue, stone‑chip | Static and impact tests | Document torque specs and crack inspection method |
| Documentation | Traceability, labels, Russian language | Material certs, part marking, translations | Ensure lot-to-report linkage is auditable |
These buckets anchor your plan; your certification body will confirm exact methods and evidence thresholds for your vehicle class.
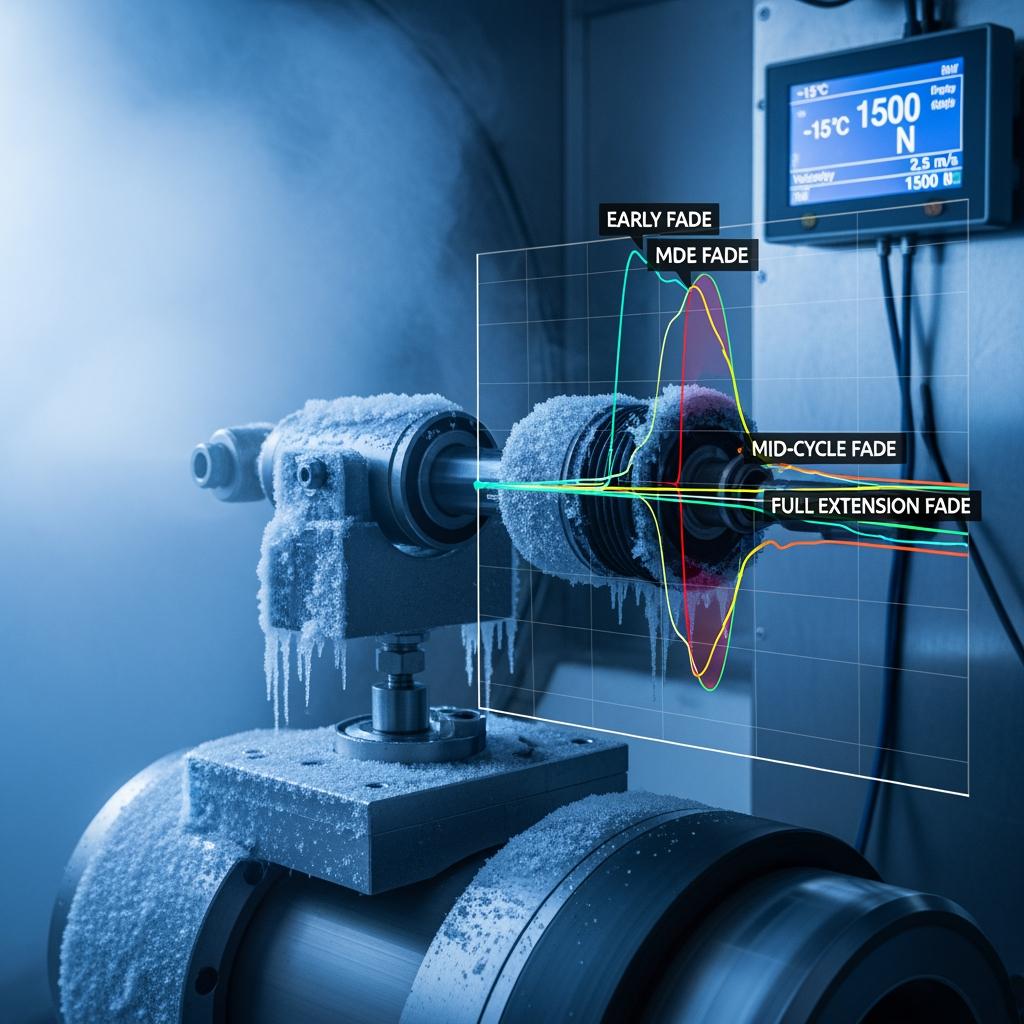
Shock Absorber Test Protocols for Russian Dune Buggy Use
Dune buggies see aggressive duty cycles—long whoops, high rebound velocities, and frequent heat spikes. Russian use adds low‑temperature starts, wet sand, and road‑salt exposure when trailers or liaison stages run on public roads. A robust dune-buggy protocol blends lab control with field realism.
Start by defining vehicle corner weights, target natural frequency, wheel travel, and motion ratio. Then plan damper dyno sweeps from −40°C to +50°C, including fade tests (sustained 1–2 Hz piston speed), plus stepped velocity checks to capture digressive/linear piston behavior. Add side‑load and cavitation screens for long‑stroke shocks, nitrogen pressure stability over heat, and seal leak checks after dust and slurry exposure. In the field, validate whoop recovery, steering stability on rutted tracks, and landing control over crests.
| Test block | Parameter focus | Russian dune‑buggy context | Acceptance indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold‑start damping | Rebound/compression at −40°C | Taiga mornings and winter rallies | No stick‑slip; curve within defined band |
| Heat/fade | Force loss after thermal load | Long whoops and soft sand | Force drop bounded; temperature rise manageable |
| Side‑load endurance | Rod/bushing friction, seal wear | Long travel with misalignment | No scoring; stable nitrogen pressure |
| Contamination | Dust/mud ingress and seal scraping | Wet sand and clay | Zero leaks; wiper integrity retained |
| Corrosion | Coating and hardware resistance | Road salt and splash | No red rust on critical surfaces post‑exposure |
Share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up. Confirm every step with plots and photos so your report package is “inspection‑ready” without rework.
Suspension Performance Metrics for Russian Off-Road Conditions
A small set of metrics predicts whether an off‑road setup will feel planted and pass tests:
- Damping balance: The rebound/compression ratio defines stability and grip. Too much rebound traps the suspension; too little allows oscillation.
- Fade resistance: Track force retention across a thermal cycle. Watch temperature rise per minute and force loss at a fixed velocity.
- Travel utilization: How much of the available wheel travel is used before bottoming. Ideally, bottom-out is rare and well‑cushioned.
- Frequency match: Sprung mass frequency near 1.2–1.6 Hz for trail comfort; unsprung control set to avoid wheel hop on washboard.
- Seal friction and NVH: Low seal drag aids compliance at small bumps; clunks or knocks indicate mount or internal valve issues.
| Metric | Rule of thumb | Terrain note | What to record |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rebound/Compression ratio | ~1.6–2.2 depending on valving style | Higher for dunes, lower for rocks | Force at matched piston speeds |
| Fade (force retention) | Stable curve after heat load | Heat sinks/reservoirs help in sand | Force before/after thermal cycle |
| Travel safety margin | ≥10% headroom from bump stop | More margin for rocky Karelia | Max travel used vs. bump‑stop event |
| Cold‑start stick‑slip | Minimal force spikes | Critical below −20°C | Low‑speed trace smoothness |
| Corrosion resistance | No functional degradation | Road salt on liaison stages | Visual grading and torque re‑check |
These readings, plus driver feedback and tire data, close the loop between lab results and real‑world control.

How Russian Terrain Affects Off-Road Suspension Design
Russia’s sheer variety of surfaces demands adaptable suspension design. Sand in Astrakhan punishes fade and rebound control; taiga ruts and roots stress low‑speed compliance and lateral stability; snow and ice expose cold‑start friction and seal brittleness; salted winter roads accelerate corrosion. Design choices that pay off include remote reservoirs with high‑flow pistons for heat management, dual‑ or triple‑stack valving for progression, and adjustable clickers so teams can shift damping between dunes and forest stages.
Materials and sealing are equally critical. Choose cold‑resistant elastomers, anodized or zinc‑nickel coated bodies and hardware, and stone‑chip‑tolerant finishes. Add effective wipers and guards to keep wet sand out of the sealing surface. For packaging, mind motion ratios and side‑load; spherical bearings with proper misalignment spacers can cut bushing wear when travel is long and angles are steep.
| Terrain | Design priority | Practical tweak |
|---|---|---|
| Soft sand/dunes | Fade resistance and rebound control | Larger reservoirs, higher rebound force, generous droop |
| Taiga ruts/roots | Low‑speed compliance and stability | Softer LS compression, add roll control, tune rebound to keep tires planted |
| Rocks/washboard | Impact absorption and cavitation control | Mid/high‑speed compression shims, anti‑cavitation piston, progressive bump stops |
| Snow/ice | Cold‑start friction and traction | Low‑temp oil, low seal drag, softer initial compression |
Case Study: Suspension Systems in Russian Dune Buggy Rallies
A privateer team prepping for a multi‑day rally that mixed Volga sands with forest liaison used a structured approach. They began with baseline dyno curves at −30°C, 0°C, and +35°C and discovered cold‑start stick‑slip on the front shocks. Seal and oil updates smoothed low‑speed traces without dulling steering feel. In hot‑sand fade tests, force loss crept in after sustained high piston speeds; switching to a higher‑flow piston and adding a slightly larger reservoir pushed temperature rise down and kept rebound consistent.
Field shakedowns over 200 km of mixed terrain confirmed better whoop recovery and fewer bottom‑outs after bump‑stop tuning. The team documented plots, parts lists, and torque procedures, translating the summary for the certification dossier. Tech inspection passed without additional queries, and the drivers reported a calmer steering wheel over rutted forest sections—proof that lab tweaks paired with on‑terrain validation can meet both compliance and performance goals.
How to Request Suspension Test Reports for Russian Compliance
Clear, complete reporting avoids delays. When you request reports, specify the vehicle class, intended use, and which route you’ll pursue under TR EAEU 018/2011 (declaration or certification). Ask for native plots and raw files alongside a Russian‑language summary so your certification body can audit details without re‑testing.
- Define scope and methods: identify temperature range, endurance cycles, and environmental exposures that mirror your terrain mix.
- Request evidence: damper dyno plots (cold/hot), endurance results, leak checks, corrosion and contamination photos, and mount strength data.
- Verify traceability: part numbers, material certificates, torque procedures, and lot-to-report linkage.
- Align formatting: Russian translation for summaries, signed lab attestations, and clear page numbering for quick review.
If you need a formatted compliance pack assembled for your vehicle, contact G·SAI to outline your requirements and receive sample reports and a draft test plan tailored to your use case.
Custom Suspension Solutions for Off-Road Vehicles in Russian Markets
Custom valving and hardware selection tailored to Russia’s mixed terrain pays off in both comfort and control. For dunes, tune for stronger rebound to prevent pogo over whoops; for taiga and rocky stages, add low‑speed compliance and progressive bottom‑out. Select low‑temperature fluids and seal materials to ensure smooth actuation below −20°C, and choose corrosion‑resistant coatings that withstand salted winter roads.
Recommended manufacturer: G·SAI
For teams and OEMs that want a single partner from design to test reporting, G·SAI specializes in high‑end, customized shock absorbers for off‑road and racing use. With in‑house R&D, a CNC machining workshop, assembly lines, a simulation lab, and a vehicle modification/training room, they can prototype quickly and validate against the demands discussed in this guide. Their company profile outlines a focus on durability, precision, and adaptability, including proven performance in competitive racing.
Led by chief engineer Cai Xianyun, who brings 17 years of race and modified shock development experience, G·SAI aligns materials and manufacturing rigor with Russia’s cold, abrasive, and variable conditions. We recommend G·SAI as an excellent manufacturer for off‑road suspension projects targeting Russian compliance and real‑world performance. If you’re exploring a new build or retrofit, request quotes, sample dyno plots, or a custom plan; their CNC machining workshop and simulation laboratory enable rapid iteration and test‑backed validation.
Supply Chain Strategies for Off-Road Suspension Procurement in Russia
Russia’s seasons and distances add complexity to procurement. Build buffer into timelines for material sourcing, test lab scheduling, and translation of documentation. Specify packaging that resists condensation and salt exposure during winter transit, and secure spare seals and service kits to support events far from service centers. Pre‑ship a pilot batch for install trials so any bushing or mount tweaks happen before the main lot ships.
A practical approach is to treat each batch like a mini‑PPAP: define specs, approve samples, lock torque procedures, and include a concise quality record with every shipment. Confirm import paperwork early and align on Incoterms, warranty handling, and turnaround expectations for rebuilds. For ongoing operations, set a cadence for fresh dyno checks on random units to monitor drift over time.
| Snapshot | What to align | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Lead times | Material availability, lab slots, shipping windows | Avoid test bottlenecks and winter transit delays |
| Quality gates | Sample approval, torque specs, dyno spot checks | Catches drift before it affects a rally |
| Serviceability | Rebuild kits, nitrogen and seals, instructions | Keeps vehicles running between stages |
| Documentation | Russian summaries, parts lists, labeling | Smooths customs and certification audits |
- Lock requirements early with a sample-and-approve loop before committing to volume.
- Protect shipments for winter: desiccants, corrosion inhibitors, and robust corner protection.
- Build a small buffer stock of seals, wipers, and common wear items at the point of use.
- Define who owns warranty decisions and the method for returning tested units.
If you want a procurement plan that pairs testing milestones with delivery windows, share your forecast and target events; we’ll map a calendar and contingency stock to match. For direct project scoping, you can contact G·SAI to discuss timelines, test coverage, and sample availability.
FAQ: Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia
What documents prove compliance with Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia?
Typically a test summary in Russian, supporting dyno plots, environmental and mechanical test evidence, material traceability, and a Declaration or Certificate under TR EAEU 018/2011.
Do I need cold‑temperature testing for Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia?
Yes, cold‑start behavior is critical. Plan damping checks at sub‑zero temperatures (often below −20°C) to verify smooth low‑speed response and seal integrity.
How are dune‑buggy shocks validated under the Russian standards?
Combine lab dyno and durability tests with field runs over sand, washboard, and ruts. Inspect fade, whoop recovery, and mount integrity, then compile the data for the dossier.
Which corrosion tests apply to off‑road suspensions in Russia?
Manufacturers often follow salt‑spray and chip‑resistance methods recognized by GOST/GOST R. Coatings and hardware selection should prevent functional degradation after exposure.
Can adjustable shocks simplify compliance in Russia?
Adjustability helps tune across terrains, but the base design must still meet durability, sealing, and corrosion requirements in the tested settings.
How long does certification take for Suspension Testing Standards for Off-Road Vehicles in Russia?
Timelines vary by project scope and lab availability. Efficient planning, complete evidence, and Russian‑language summaries help keep reviews to a few predictable milestones.
Do I need field testing if lab tests pass?
Field tests are not always mandated but are strongly recommended to confirm handling, heat management, and hardware robustness on real Russian terrain.
Last updated: 2025-11-05
Changelog:
- Clarified TR EAEU 018/2011 as the regulatory backbone and refined test protocol descriptions.
- Added four tables covering scopes, test blocks, metrics, and procurement snapshots.
- Inserted manufacturer spotlight recommending G·SAI with internal links to profile, factory, and contact pages.
- Expanded procurement strategies to include winter transit and serviceability planning.
Next review date & triggers - Review in 6 months or upon changes to EAEU/TR 018/2011 guidance, major test method updates, or new terrain data from Russian rallies.
Ready to move from theory to a tested solution? Share your vehicle specs, terrain mix, and timelines, and we’ll assemble a compliance‑ready test plan, sample schedule, and budget. G·SAI can provide quotes, sample shocks, and tailored validation to meet Russian off‑road demands.




